Electronic Component Description
1-2
and 2-3 Shift Solenoid Valves
Important
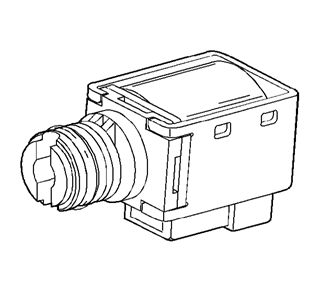
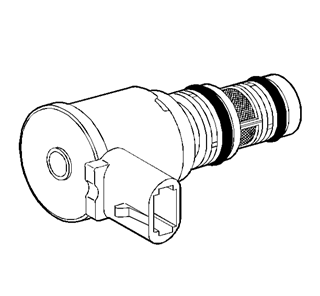
The shift solenoid valve
resistance should measure 19-24 ohms minimum when measured at 20°C (68°F).
The shift solenoid current flow should not exceed 0.75 amps. The shift
solenoid should energize at a voltage of 7.5 volts or more (measured
across the terminals). The shift solenoid should de-energize when the voltage
is one volt or less.
If both solenoids lose power,
third gear only results.
The 1-2 and 2-3 shift
solenoid valves (also called A and B solenoids) are identical devices that
control the movement of the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves (the 3-4 shift valve is
not directly controlled by a shift solenoid). The solenoids are normally open
exhaust valves that work in four combinations to shift the transmission into
different gears.
The PCM energizes each
solenoid by grounding the solenoid through an internal quad driver. This sends
current through the coil winding in the solenoid and moves the internal plunger
out of the exhaust position. When ON, the solenoid redirects
fluid to move a shift valve.
Important
The manual valve
hydraulically can override the shift solenoids. Only in D4 do the shift
solenoid states totally determine what gear the transmission is in. In the
other manual valve positions, the transmission shifts hydraulically and the
shift solenoid states CATCH UP when the throttle position and the vehicle speed
fall into the correct ranges. Diagnostic trouble codes P0753 and P0758 indicate
shift solenoid circuit voltage faults.
The PCM-controlled shift
solenoids eliminate the need for TV and governor pressures to control shift
valve operation.
3-2
Shift Solenoid Valve Assembly
Important
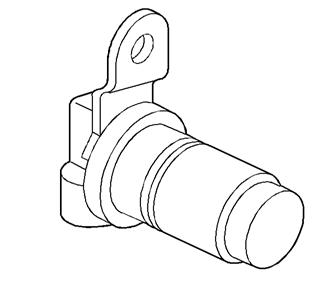
The 3-2 shift solenoid valve
assembly resistance should be a minimum of 20-24 ohms at 20°C (68°F).
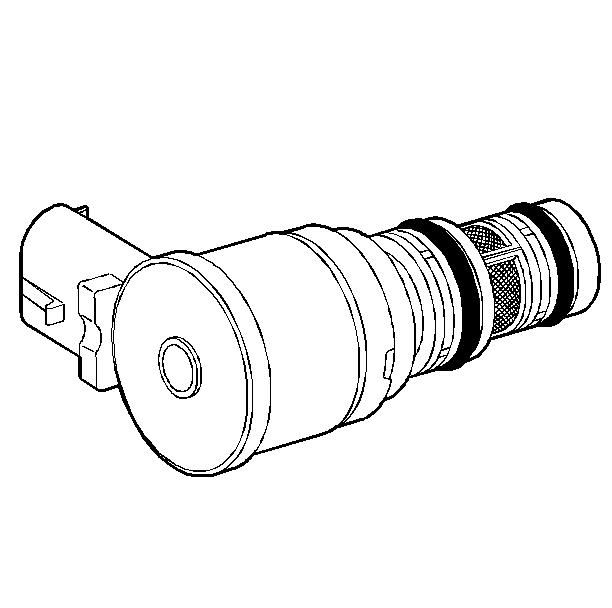
The 3-2 shift solenoid
valve assembly is an ON/OFF solenoid that is used in order to improve the 3-2
downshift. The solenoid regulates the release of the 3-4 clutch
and the 2-4 band apply.
If a voltage fault is
detected in the 3-2 shift solenoid circuit, diagnostic trouble code P0785 will
set.
Transmission
Pressure Control Solenoid
Important
Transmission pressure control
solenoid resistance should measure 3-5 ohms when measured at 20°C (68°F).
The transmission
pressure control solenoid is an electronic pressure regulator that controls
pressure based on the current flow through its coil winding. The magnetic field
produced by the coil moves the solenoid's internal valve which varies pressure
to the pressure regulator valve.
The PCM controls the
pressure control solenoid by commanding current between 0.1 and 1.1 amps. This changes the duty cycle of the solenoid, which can range
between 5 percent and 95 percent (typically less than
60 percent). 1.1 amps corresponds to minimum
line pressure, and 0.1 amps corresponds to maximum line pressure (if the
solenoid loses power, the transmission defaults to maximum line pressure).
The PCM commands the
line pressure values, using inputs such as the throttle position sensor.
The pressure control
solenoid takes the place of the throttle valve or the vacuum modulator that was
used on the past model transmissions.
If the duty cycle drops
below 5 percent or rises above 95 percent, DTC P0748 will set.
Torque
Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve
Important
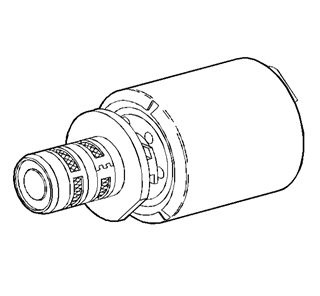
The TCC solenoid resistance
should be 21-26 ohms minimum when measured at 20°C (68°F).
If a fault is detected
in the TCC solenoid circuit, code P0740 will set.
The torque converter
clutch solenoid valve is a normally open exhaust valve that is used to control
torque converter clutch apply and release. When grounded (energized) by the
PCM, the TCC solenoid valve stops converter signal oil from exhausting. This
causes converter signal oil pressure to increase and shifts the TCC solenoid
valve into the apply position.
The brake switch is an
input to the PCM, and the PCM directly controls the TCC apply based on the
brake switch status.
Torque
Converter Clutch PWM Solenoid Valve
Important
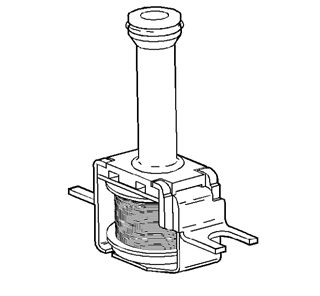
TCC PWM solenoid valve
resistance should be 10-11 ohms when measured at 20°C (68°F),
and 13-15 ohms when measured at 100°C (212°F).
The torque converter
clutch PWM solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter clutch
valve, which then controls the TCC apply and release. This solenoid is attached
to the control valve body assembly within the transmission. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides smooth engagement of the torque converter clutch by
operating on a negative duty cycle a variable percent of ON time.
If a fault is detected
in the TCC PWM circuit, code P1860 will set.
Transmission
Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual Valve Position Switch
Important
Seven valid combinations and
two invalid combinations are available from the TFP manual valve position
switch. Refer to the Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual Valve Position
Switch Logic table for valid/invalid combinations for range signal circuits
A, B and C.
The transmission fluid
pressure (TFP) manual valve position switch is a set of five pressure switches
on the control valve body that sense whether fluid pressure is present in five
different valve body passages. The combination of which switches are open and
closed is used by the PCM in order to determine actual manual valve position. The
TFP manual valve position switch, however, cannot distinguish between PARK and
NEU
The switches are wired
to provide three signal lines that are monitored by the PCM. These inputs are
used to help control line pressure, torque converter clutch apply and shift
solenoid valve operation. Voltage at each of the signal lines is either zero or
twelve volts.
In order to monitor the
TFP manual valve position switch operation, the PCM compares the actual voltage
combination of the switches to a TFP combination table stored in its memory. If
the PCM sees one of two illegal voltage combinations, a DTC P1810 will
result. A DTC P1810 indicates a short circuit condition in either the
range signal A or the range signal C
circuits.
The TFP manual valve
position switch signal voltage can be measured from each pin-to-ground and
compared to the combination table. On the automatic transmission (A/T) wiring
harness assembly, pin N is range signal A,
pin R is range signal B, and pin P is range signal C. With
the A/T wiring harness assembly connected and the engine running, a voltage
measurement of these three lines will indicate a high reading (near
12 volts) when a circuit is open, and a low reading (zero volts) when
the circuit is switched to ground.
The transmission fluid
temperature (TFT) sensor is part of the TFP manual valve position switch
assembly.
Important
The sensor resistance is
model dependent and varies with speed from a minimum of 0.5 volts AC at
100 RPM to more than 100 volts AC at 8000 RPM.
The vehicle speed sensor
(or transmission output speed sensor) controls shift points and calculates the
TCC slip.
The speed sensor
contains a coil that gives off a continuous magnetic field. A rotor rotates
past the sensor and the rotor teeth break the magnetic field. Each break in the
field sends a pulse to the VSSB (Vehicle Speed Sensor Buffer). The VSSB sends
two signals to the PCM. The first is a 2002 pulse per mile (PPM) signal that is
used by the engine. The second is the transmission/transfer case 40 pulse per revolution (PPR) signal that is used in order to
control the transmission.
In two wheel drive (2WD)
applications, the vehicle speed sensor is located on the transmission extension
housing. Trans Output Speed = Transfer Case Speed.
DTC P0502 will set
if a fault exists in the vehicle speed sensor circuit 40 PPR line.
Automatic
Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
The automatic
transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor is part of the automatic
transmission fluid pressure (TFP) manual valve position switch assembly. This
sensor helps control torque converter clutch apply and shift quality.
The TFT sensor is a
resistor, or thermistor, which changes value based on
temperature. At low temperatures the resistance is high, and at high
temperatures the resistance is low.
The PCM sends a
5 volt signal to the TFT sensor and the PCM measures the voltage drop in
the circuit. You will measure a high voltage when the transmission is cold and
a low voltage when the transmission is hot. Refer to the Temperature vs Resistance table.
If the TFT sensor circuit
has a fault, DTC P0712 or P0713 is set. A DTC P0712 indicates a short
circuit condition, while a DTC P0713 indicates an open circuit condition.
DTC P0218 is set if the transmission is operating at a high temperature
for a period of time.